Below is good blog post which explains why reducing diesel exhaust Particulate Matter is important for slowing global warming as well as improving human health.
For more on this subject, see;
Cleaning up Diesel Exhaust Improves both Health and Climate
California’s Diesel Control Program and its Black Carbon Co-benefits
——————————————————————————-
Black carbon – a health and environment issue
Source: Terra et Aqua blog
By Rob Ellison
Regardless of net climate forcing or other climatic effects, all black carbon mitigation options bring health benefits through reduced particulate matter exposure
‘The best estimate of industrial-era climate forcing of black carbon through all forcing mechanisms, including clouds and cryosphere forcing, is +1.1 W/m 2 with 90% uncertainty bounds of +0.17 to +2.1 W/m 2. Thus, there is a very high probability that black carbon emissions, independent of co-emitted species, have a positive forcing and warm the climate. We estimate that black carbon, with a total climate forcing of +1.1 W/m 2, is the second most important human emission in terms of its climate forcing in the present-day atmosphere; only carbon dioxide is estimated to have a greater forcing…’ Bond, T. C. et al, 2013, Bounding the role of black carbon in the climate system: A scientific assessment, JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH: ATMOSPHERES, VOL. 118, 5380–5552, doi:10.1002/jgrd.50171
Figure 1: Schematic of black carbon source and processes (Bond et al, 2013)
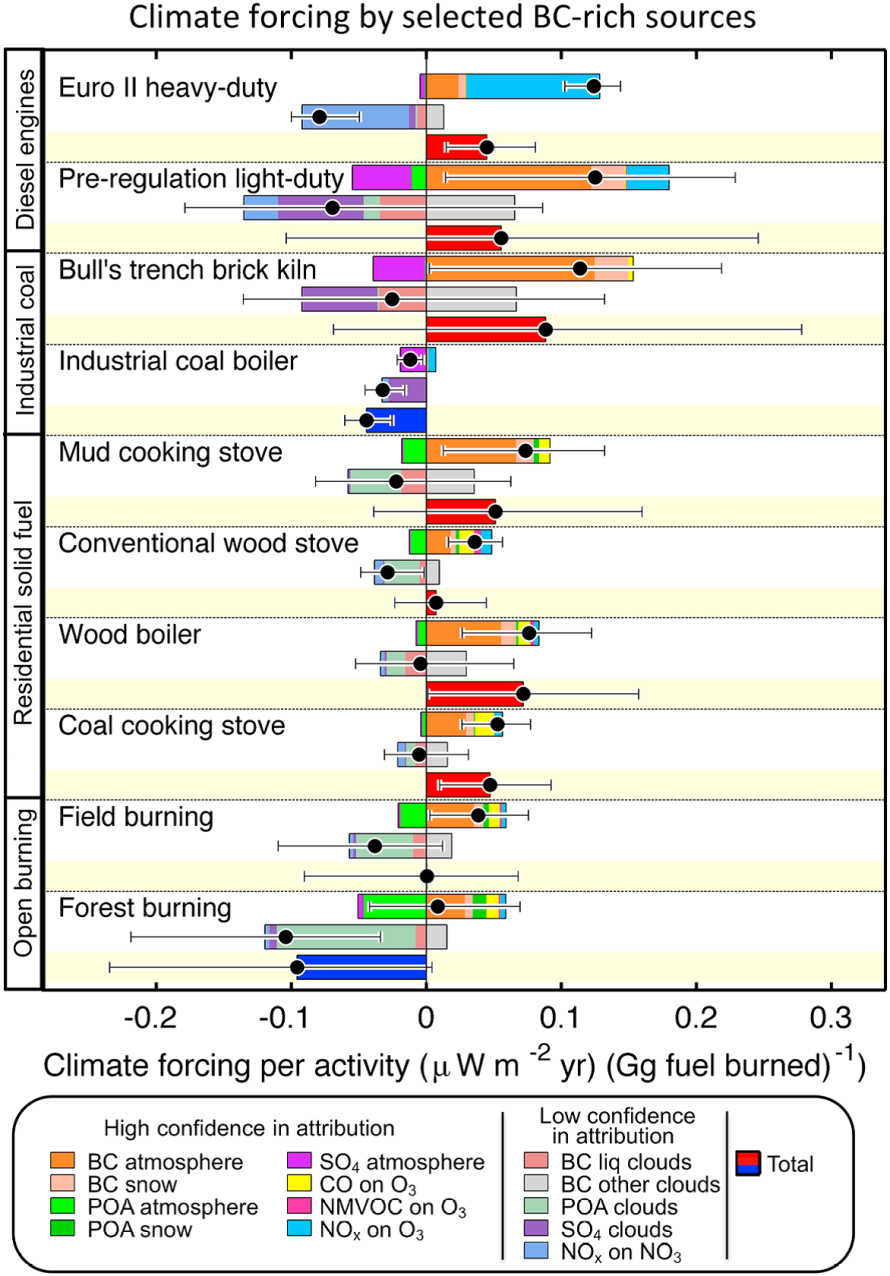
The net effect of black carbon in the atmosphere depends on cloud effects and co-emitted gases and aerosols. Climate forcing from diesel engines, brick kilns and residential solid fuel stoves are net positive – shown in the red bars below. Burning of fields and forest forcings do not include CO2 emissions from land use changes or loss of soil organic carbon.
Figure 2: Net forcing from BC sources (Source: Bond et al 2013)
Black carbon emissions increase with industrialisation and then fall off rapidly. This can be seen in the relative size of regional emissions.
Figure 3: Emission rates of BC in the year 2000 by region, indicating major source categories in each region (Source: Bond et al 2013)
Mitigation with existing technology is well underway.
Diesel Engines
‘On-road diesel engines include diesel cars and trucks, while off-road engines include engines used in agriculture, construction, and other heavy equipment. The diesel-engine category in this assessment specifically excludes shipping emissions, which are summarized separately. Diesel engines contributed about 20% of global BC emissions in 2000. These sources have the lowest co-emissions of aerosols or aerosol precursors of all the major BC sources. In order to enable use of the most advanced exhaust controls, sulfur must be removed from the diesel fuel during refining. Therefore, in regions with fewer controls, primary particulate matter emission factors are higher, but SO2 emissions are also higher….
Diesel engine sources of BC appear to offer the best mitigation potential to reduce near-term climate forcing. In developed countries, retrofitting older diesel vehicles and engines is a key mitigation strategy; in developing countries, transitioning a growing vehicle fleet to a cleaner fleet will be important.’ Bond et al 2013
Figure 4: Improvements in diesel engine emissions
Essentially this appears to be business as usual. Replacement of older equipment with newer and more efficient equipment.
Industrial Coal
‘Industrial coal combustion is estimated to provide about 9% of global emissions, mainly in small boilers, process heat for brick and lime kilns, and coke production for the steel industry. Although coal combustors can be designed to produce little BC, coal can also be highly polluting when burned in simple combustors, which are still present in small industries, particularly in developing countries. Co-emitted SO2 is estimated from coal sulfur content and exhaust control. The SO2/BC ratio for industrial coal is much higher than that for the other emission categories, where the fuel has little sulfur or more efficient flue-gas controls are in place. Emissions from coal-fired power plants, which emit much less BC because of their better combustion efficiency, are not included here.’ Bond et al 2013
Residential Solid Fuels
‘Wood, agricultural waste, dung, and coal are used for cooking or heating in homes, providing another 25% of BC emissions. Most of the emissions occur in single-family devices, which are often of simple design. When infrastructure and income do not allow access to low-emission residential energy sources such as electricity and natural gas, solid fuels are used extensively for cooking. Otherwise, they are used more often for heating. Coal and, less frequently, wood are also used for heating in multi-family building boilers. The designation “cooking” in Figure 2 refers to regions where wood is primarily used for cooking, even if some heating occurs. Similarly, “heating” includes all uses in regions where heating is dominant. This sector also includes emissions from both production and consumption of charcoal. The poor combustion and mixing in these simple devices result in relatively high POA:BC ratios, but SO2 emissions are low except for coal.’ Bond et al 2013
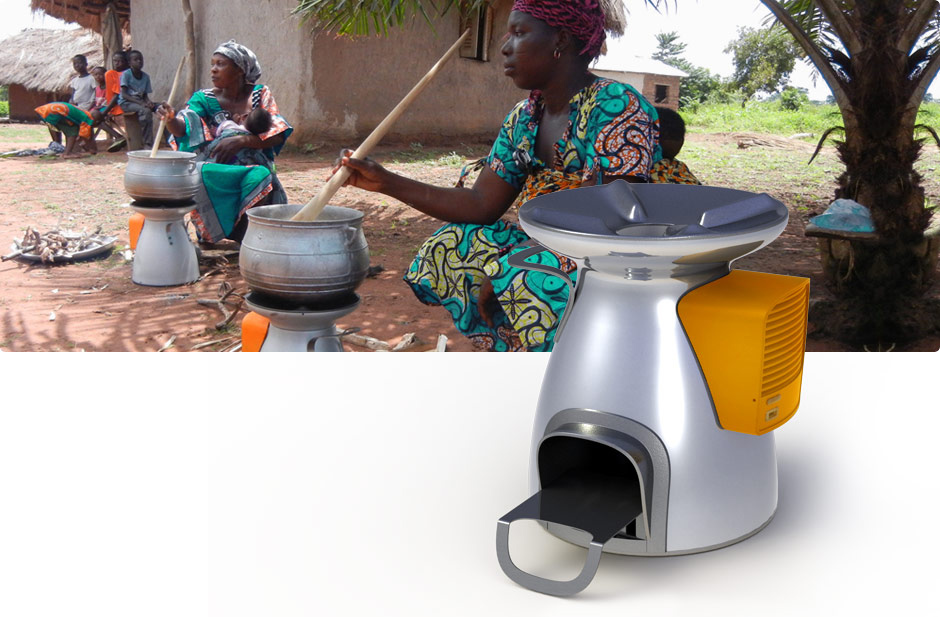
Figure 5: Biolite home stove
50% Less Wood Consumed Time and Cash Savings
95% Smoke Reduction Improved Health
Nearly Eliminates Black Carbon Protects Climate
Generates Electricity Charges Phones & LED Lights
As well as prevention of millions of premature deaths.
Open Burning
‘Open burning of biomass in the location where it is grown is a very large contributor to global BC emissions, with bottom-up estimates predicting that it contributes about 40% of the total… Current global emissions estimated from open burning range between 2000 and 11,000 Gg/yr for BC and between 18,000 and 77,000 Gg/yr for OC in average years… Most studies fall into the range of 2000 to 6000 Gg/yr for BC and 20,000 to 27,000 Gg/yr for OC… A smaller contribution originates from open burning in agricultural fields, which is often done to clear residues after harvest. This source contributes about 300 Gg/yr BC and 1500 Gg/yr OC. In regions like south Asia, this source can contribute about 20% of carbonaceous aerosol emissions.’ Bond et al 2013
Crop residue is far better preserved in soil carbon than burnt –https://watertechbyrie.com/2014/06/26/food-for-people-conserving-and-restoring-soils/
Some forest types are adapted to burning – but if it results in land use change the carbon impacts are a significant factor in climate change.
Figure 6: Carbon dioxide emissions by source
When black carbon is factored in – carbon dioxide from fossil fuels is the smaller part of the problem. Reduction in black carbon emissions are feasible with existing technology, relatively inexpensive, has the potential to save lives and can provide large scale mitigation of climate impacts.
Aside This entry was posted in Focus Area 1, Focus Area 10, Focus Area 11, Focus Area 14, Focus Area 15, Focus Area 2, Focus Area 3, Focus Area 7, Focus Area 8, Focus Area 9 and tagged black carbon, climate change, energy, greenhouse gas emissions, greenhouse gas mitigation, industrialization, production. Bookmark the permalink.






One Response to Black carbon – a health and environment issue